Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) detects objects in images using a single deep neural network. In this blog post I will cover how to implement SSD300 (meaning images are scaled to 300x300 before being fed to the model) detector presented here in Tensorflow 2.0.
What do we Need?
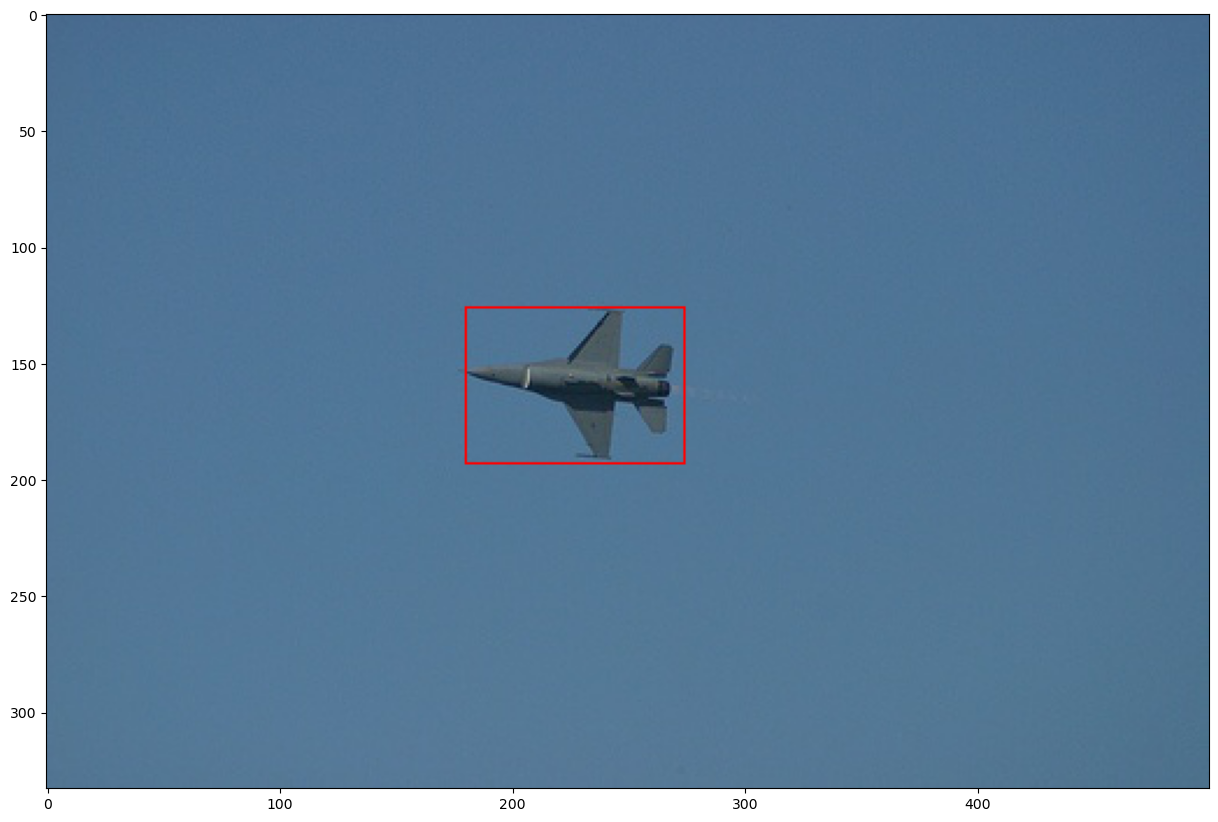
To train an SSD model, we need an input image with ground truth boxes for each objects. The figure below shows an example of an image with a ground truth label for aeroplane:

In addition we also need default boxes (also called anchor boxes). At training time, the default boxes are matched to the ground truth boxes. The image below shows all of the default boxes that overlap with the ground truth box.
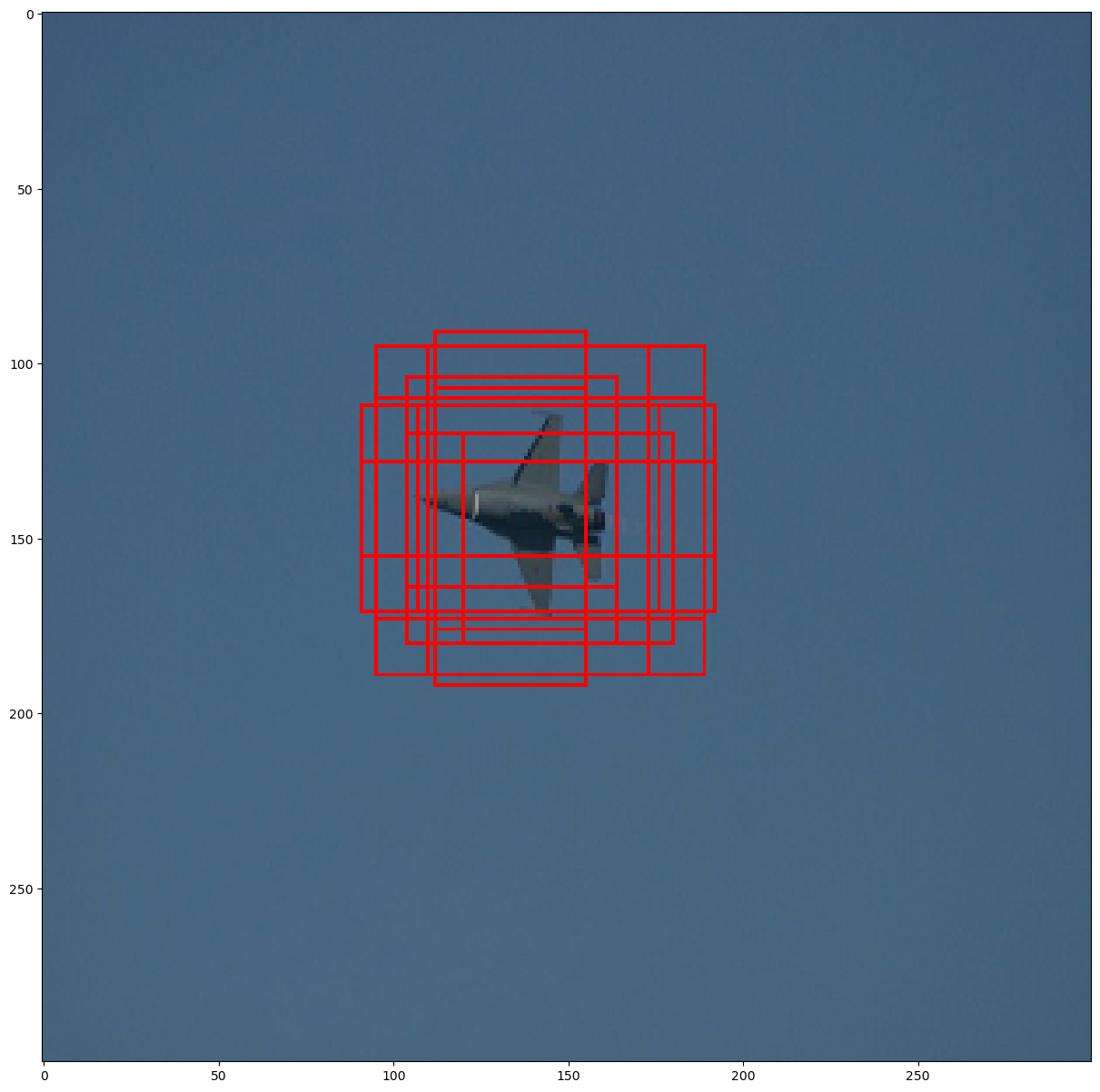

The matched boxes are treated as positives and the rest of the default boxes are treated as negative.
Model Configuration
The SSD approach produces a fixed-size collection of default boxes. The model then predict the offset and classification scores for each of the default boxes. The early network layers are based on standard architecture used for image classification (VGG16, VGG19, MobileNetV1, MobileNetV2, etc.). Auxilary structure is added to the base model to produce the offset and classification scores for the default boxes. In this blog I will be going over how to use VGG16 as the base model layer and build a SSD model off off it.
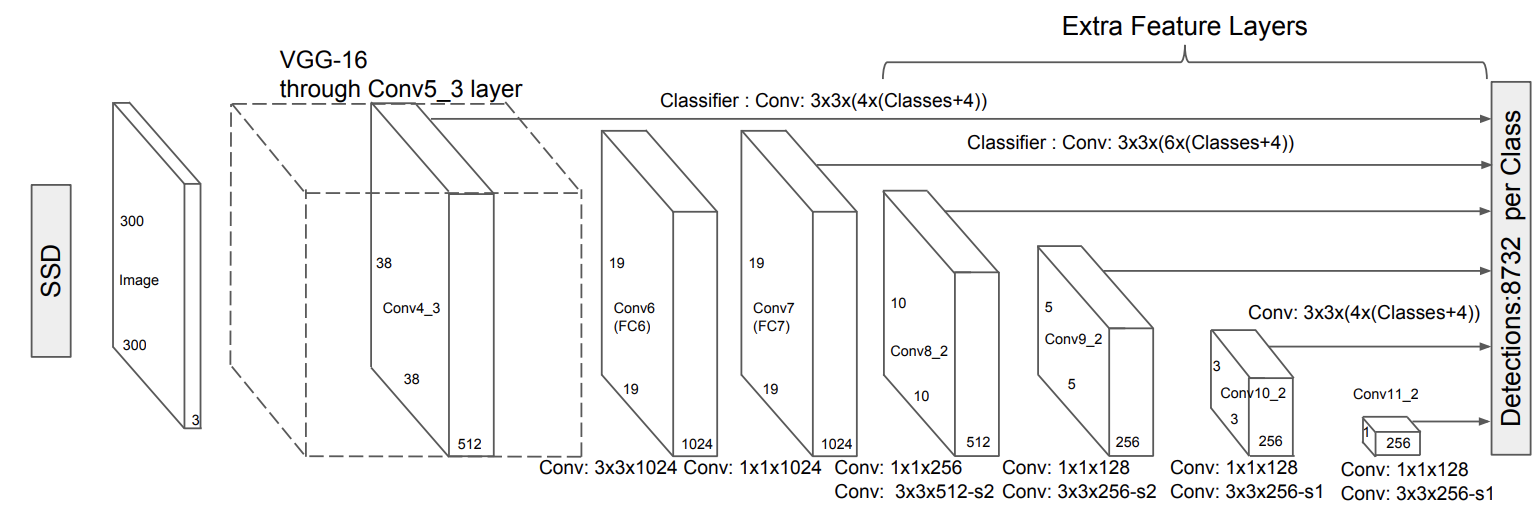
In SSD, the tiles of convolution kernels map to the default boxes. The goal is to predict the offsets of the default boxes and the class scores. In the image below, we can see how the CNN output maps to the default boxes for an image.
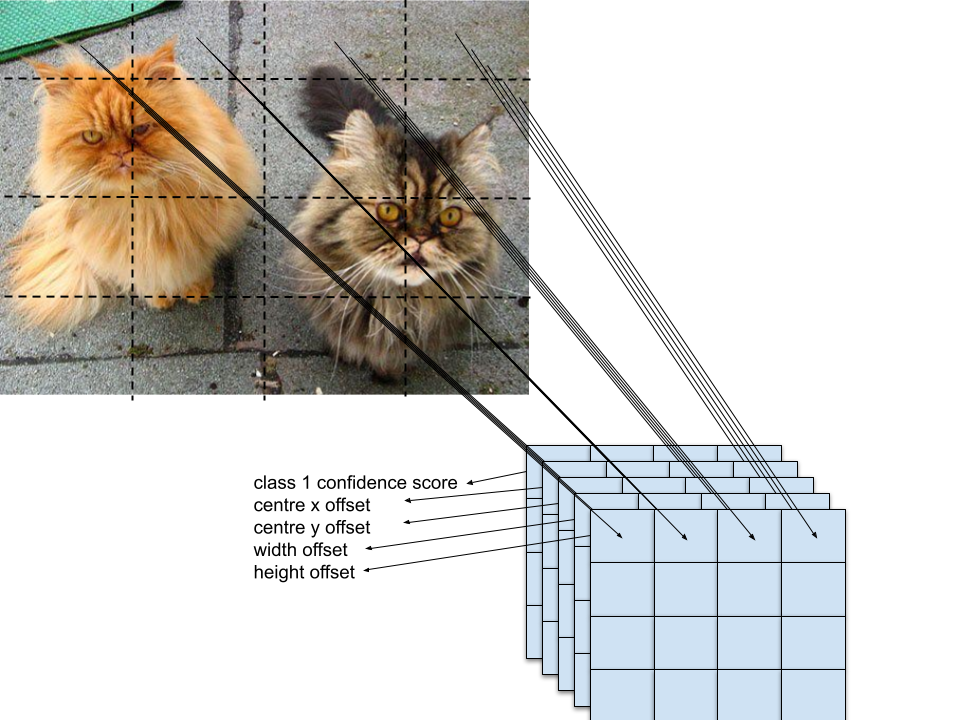
For each default box we generate $(4 + c + 1)$ outputs, where 4 because of the offsets, $c$ is the number of classes in the dataset and +1 for background. To detect an object at muliple scales within a dataset SSD uses multi-scale feature maps for detections at multiple scales.
Matching Default Boxes to Ground Truth Boxes
To train the model we need to determine which default boxes correspond to ground truth detection. Each ground truth box is matched to the default box with the highest Intersect over Union (IOU). We then also match default boxes to any ground truth boxes with IOU > threshold (set as 0.5).
Training Objectives
The loss function for the SSD model is the weighted sum of the localization loss and the confidence loss:
\[L(x, c, l, g) = \dfrac{1}{N}(L_{conf}(x,x) + \alpha L_{loc}(x,l,g))\]where
- $N$ is the total number of matched default boxes, edge case: if N = 0 then set loss to 0,
- $x$ is an indicator for matching the $i$-th default boxes to the $j$-th ground truth box,
- $l$ is the predicted box,
- $g$ is the ground truth box,
- $c$ is the predicted class,
- $\alpha$ is set to 1.
For the localization loss we regress to offsets for the $(cx, cy, w, h)$ of the matching default bounding boxes.
\[L_{loc}(x,l,g) = x_{ij}^p\sum^N_{i \in Pos} \sum_{m \in \{cx, cy,w,h \}}smooth_{\text{L1}}(l_i^m - \hat{g}_j^m)\]where
\[\hat{g}_j^{cx} = 5 * \dfrac{g_j^{cx} - d_i^{cx}}{d_i^w} \\ \hat{g}_j^{cy} = 5 * \dfrac{g_j^{cy} - d_i^{cy}}{d_i^h} \\ \hat{g}_j^{w} = 10 * \text{log}\left(\dfrac{g_j^w}{d_i^w}\right) \\ \hat{g}_j^{h} = 10 * \text{log}\left(\dfrac{g_j^h}{d_i^h}\right) \label{eq:offsets}\]and
\[x_{ij}^p = \begin{cases} 1, ~~~ \text{if IOU > threshold between default box } i \text{ and ground truth box } j \text{ on class } p \\ 0, ~~~ \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\]The prior variances or the scaling constants (5 and 10 in Eq. \ref{eq:offsets}) are not mentioned in the paper, but they are used in the code, I read about them here. The author of the paper suggests in a github comment that they can also be understood as loss smoothing factors, the confidence and the localization loss are on a different scale and using the scaling constants brings these two losses together allowing for a smoother loss function that is easier to optimize.
The confidence loss is the softmax loss over multiple classes:
\[L_{conf}(x,c) = -\sum_{i \in Pos}^N x_{ij}^p log(\hat{c}_i^p) - \sum_{i \in Neg}log(\hat{c}_i^0) \\ \hat{c}_i^p = \dfrac{ e^{c_i^p} }{ \sum_p e^{c_i^p} }\]where $\hat{c}_i^p$ is the predicted softmax probaility for the default box $i$, $\hat{c}_i^0$ is the predicted softmax probaility that that the default box is a background.
Implementing SSD in Tensorflow 2.0
Now that we have an understanding of the theory behind SSD model architecture, we can now implement the model in Tensorflow 2.0. I have already covered how to generate anchor boxes in a previous post so I will not go over them here. Once we have the default boxes we can then match these default boxes with the ground truth boxes. One thing to note is that the method to generate default boxes covered in my previous blogs outputs the boxes in centroid representation: $[cx, cy, w, h]$, to calculate IOUs between two rectangles it is best to represent to use the corners representation: $[xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax]$.
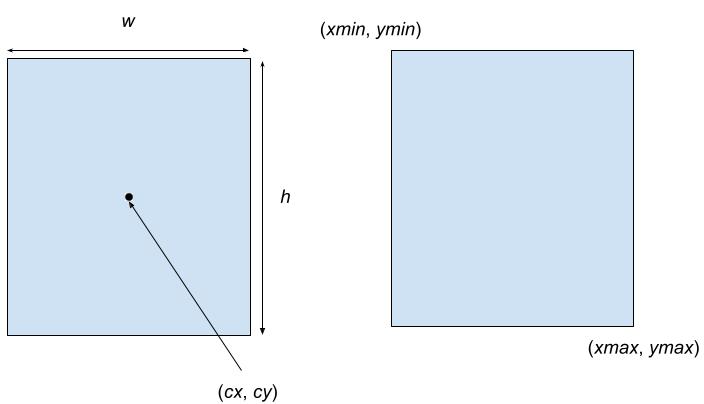 Centroid box representation on right, corner representation on left.
Centroid box representation on right, corner representation on left.
How to compute IOU?
Using the corner representation it is straightforward to calculate IOU for 2 rectangles.
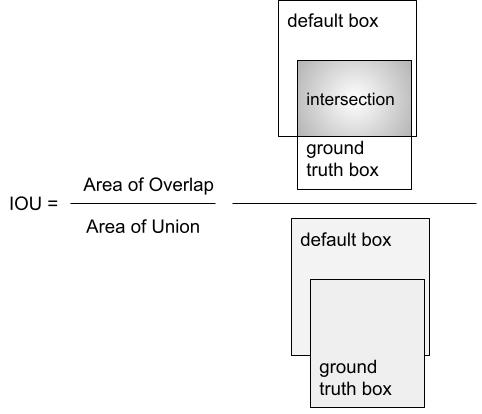
Given a pair of rectangular boxes:
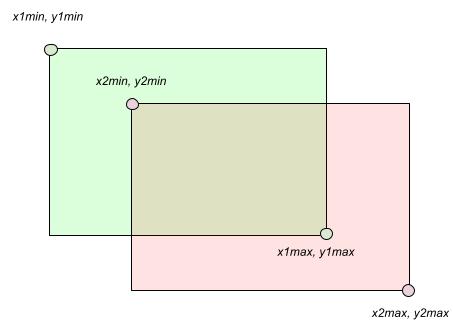
we can find the top-left coordinates of the intersecting bounding box as:
\[xi_{min} = max(x1min, x2min) yi_{min} = max(y1min, y2min)\]The bottom-right ccordinates of the intersecting box is
\[xi_{max} = min(x1max, x2max) \\ yi_{max} = min(y1max, y2max)\]The intersecting area can be easily computed from the coordinates obtained:
\[A_{inter} = max(0, yi_{max} - yi_{min}) * max(0, xi_{max} - xi_{min})\]If the rectangles don’t overlap then
\[yi_{max} < yi_{min} \text{ or } xi_{max} < xi_{min}\]in which case $A_{inter} = 0$.
The code below contains helper functions to generate default bounding boxes, find default boxes for which IOU > threshold with ground truth boxes, calculate offsets for training objectives as shown in Eq. \ref{eq:offsets}
def calculate_scale_of_default_boxes(k, m, s_max = 0.9, s_min = 0.2):
"""
m = number_of_feature_maps
s_k = s_min + (s_max - s_min) * (k - 1)/(m - 1)
width_k = s_k * sqrt(aspect_ratio)
height_k = s_k / sqrt(aspect_ratio)
"""
return s_min + (s_max - s_min) * (k - 1) / (m - 1)
def generate_default_boxes(feature_map_shapes, number_of_feature_maps, aspect_ratios):
"""
feature map shapes for VGG: [38, 19, 10, 5, 3, 1]
"""
assert len(feature_map_shapes) == number_of_feature_maps, 'number of feature maps needs to be {0}'.format(len(feature_map_shapes))
assert len(feature_map_shapes) == len(aspect_ratios), 'Need aspect ratios for all feature maps'
prior_boxes = []
for k, f_k in enumerate(feature_map_shapes):
s_k = calculate_scale_of_default_boxes(k, m = number_of_feature_maps)
s_k_prime = np.sqrt(s_k * calculate_scale_of_default_boxes(k + 1, m = 6))
for i in range(f_k):
for j in range(f_k):
cx = (i + 0.5) / f_k
cy = (j + 0.5) / f_k
prior_boxes.append([cx, cy, s_k_prime, s_k_prime])
for ar in aspect_ratios[k]:
# height, width for numpy
prior_boxes.append([cx, cy, s_k*np.sqrt(ar), s_k/np.sqrt(ar)])
prior_boxes = tf.convert_to_tensor(prior_boxes, dtype=tf.float32)
return tf.clip_by_value(prior_boxes, clip_value_min = 0., clip_value_max = 1.)
# Adapted from https://gist.github.com/escuccim/d0be49ccfc6084cdc784a67339f130dd
def box_overlap_iou(boxes, gt_boxes):
"""
Args:
boxes: shape (total boxes, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max)
gt_boxes: shape (1, total label, x_min y_min, x_max, y_max)
Returns:
Tensor with shape (batch_size, total boxes, total label)
"""
box_x_min, box_y_min, box_x_max, box_y_max = tf.split(boxes, 4, axis = 1)
gt_boxes_x_min, gt_boxes_y_min, gt_boxes_x_max, gt_boxes_y_max = tf.split(gt_boxes, 4, axis = 2)
# From https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/transpose
intersection_x_min = tf.maximum(box_x_min, tf.transpose(gt_boxes_x_min, perm=[0, 2, 1]))
intersection_y_min = tf.maximum(box_y_min, tf.transpose(gt_boxes_y_min, perm=[0, 2, 1]))
intersection_x_max = tf.minimum(box_x_max, tf.transpose(gt_boxes_x_max, perm=[0, 2, 1]))
intersection_y_max = tf.minimum(box_y_max, tf.transpose(gt_boxes_y_max, perm=[0, 2, 1]))
# need to take care of boxes that don't overlap at all
intersection_area = tf.maximum(intersection_x_max - intersection_x_min, 0) * tf.maximum(intersection_y_max - intersection_y_min, 0)
boxes_areas = (box_x_max - box_x_min) * (box_y_max - box_y_min)
gt_box_areas = (gt_boxes_x_max - gt_boxes_x_min) * (gt_boxes_y_max - gt_boxes_y_min)
union = (boxes_areas + tf.transpose(gt_box_areas, perm=[0, 2, 1])) - intersection_area
return tf.maximum(intersection_area / union, 0)
def match_priors_with_gt(prior_boxes, boxes, gt_boxes, gt_labels, number_of_labels, threshold = 0.5):
"""
prior boxes: (1, number of default boxes, c_x, c_y, w, h)
boxes: shape (total boxes, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max)
gt_boxes: (1, number of labels, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max)
gt_labels: (1, 1 label per each gt box)
0 is background, so the gt_labels is the number of labels in the dataset + 1
class 0 is reserved.
"""
# number of rows for the IOU map the is the number of gt_boxes
IOU_map = box_overlap_iou(boxes, gt_boxes)
# convert ground boxes labels to box label format
gt_box_label = convert_to_centre_dimensions_form(gt_boxes)
# select the box with the highest IOU
highest_overlap_idx = tf.math.argmax(IOU_map, axis = 1)
highest_overlap_idx = tf.cast(highest_overlap_idx, tf.int32)
idx = tf.range(IOU_map.shape[1])
highest_overlap_idx_map = tf.expand_dims(tf.equal(idx, tf.transpose(highest_overlap_idx)), axis = 0)
IOU_map = tf.where(tf.transpose(highest_overlap_idx_map, perm=[0,2,1]), tf.constant(1.0), IOU_map)
# find the column idx with the highest IOU at each row
max_IOU_idx_per_row = tf.math.argmax(IOU_map, axis = 2)
# find the max value per row
max_IOU_per_row = tf.reduce_max(IOU_map, axis = 2)
# threshold IOU
max_IOU_above_threshold = tf.greater(max_IOU_per_row, threshold)
# map the gt boxes to the prior boxes with the highest overlap
gt_box_label_map = tf.gather(gt_box_label, max_IOU_idx_per_row, batch_dims = 1)
# get the offset, offcet (delta_cx, delta_cy, delta_width, delta_height)
gt_box_label_map_offsets = calculate_offset_from_gt(gt_box_label_map, prior_boxes)
# remove from gt_boxes_map where overlap with prior boxes is less than 0.5
gt_boxes_map_offset_suppressed = tf.where( tf.expand_dims(max_IOU_above_threshold, -1),
gt_box_label_map_offsets, tf.zeros_like(gt_box_label_map))
# add a positive condition column for the localization loss
max_IOU_above_threshold_expand = tf.expand_dims(max_IOU_above_threshold, -1)
max_IOU_above_threshold_expand = tf.cast(max_IOU_above_threshold_expand, tf.float32)
gt_boxes_map_offset_suppressed_with_pos_cond = tf.concat([ gt_boxes_map_offset_suppressed,
max_IOU_above_threshold_expand ], axis = 2)
gt_labels_map = tf.gather(gt_labels, max_IOU_idx_per_row, batch_dims = 1)
# suppress the label where IOU with the gt boxes is < 0.5
gt_labels_map_suppressed = tf.where( max_IOU_above_threshold,
gt_labels_map, tf.zeros_like(gt_labels_map))
gt_labels_one_hot_encoded = tf.one_hot(gt_labels_map_suppressed, number_of_labels)
return gt_boxes_map_offset_suppressed_with_pos_cond, gt_labels_one_hot_encoded
def calculate_offset_from_gt(gt_boxes_mapped_to_prior, prior_boxes):
prior_boxes = tf.expand_dims(prior_boxes, axis=0)
g_j_cx = 10 * (gt_boxes_mapped_to_prior[:, :, 0] - prior_boxes[:, :, 0]) / prior_boxes[:, :, 2]
g_j_cy = 10 * (gt_boxes_mapped_to_prior[:, :, 1] - prior_boxes[:, :, 1]) / prior_boxes[:, :, 3]
g_j_w = 5 * tf.math.log(gt_boxes_mapped_to_prior[:, :, 2] / prior_boxes[:, :, 2])
g_j_h = 5 * tf.math.log(gt_boxes_mapped_to_prior[:, :, 3] / prior_boxes[:, :, 3])
offset = tf.concat( [ g_j_cx, g_j_cy, g_j_w, g_j_h ] , axis = 0)
return tf.transpose(tf.expand_dims(offset, axis = 0), perm=[0,2,1])
def convert_to_box_form(boxes):
"""
Input:
(number_of_labels, c_x, c_y, width, height)
Output:
(number_of_labels, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max)
"""
box_coordinates = tf.concat([ boxes[:, :2] - boxes[:, 2:] / 2,
boxes[:, :2] + boxes[:, 2:] / 2 ],
axis = 1)
return tf.clip_by_value(box_coordinates, clip_value_min = 0., clip_value_max = 1.)
def convert_to_centre_dimensions_form(boxes):
"""
Input:
boxes: (1, number_of_labels, x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max)
Output:
(1, number_of_labels, c_x, c_y, width, height)
"""
coordinates = tf.concat([
[
(boxes[:, :, 0] + boxes[:, :, 2]) / 2.,
(boxes[:, :, 1] + boxes[:, :, 3]) / 2.,
boxes[:, :, 2] - boxes[:, :, 0],
boxes[:, :, 3] - boxes[:, :, 1]
]], axis = 1)
# need the output in the same format as input, could be imporived
coordinates = tf.transpose(coordinates, perm=[1,2,0])
return tf.clip_by_value(coordinates, clip_value_min = 0., clip_value_max = 1.)
Setting up the Data Generation Pipeline
To train the model we need to setup a data generation pipeline. There is no one best way of encoding your data for the training process. I decided to split the data into two parts, one part encodes the default box offsets and the second part encodes the labels. Using this format also allows me to right seperate loss functions for the default box offset regression and for the confidence loss.
class DataGenerator(keras.utils.Sequence):
def __init__(self, list_IDs,
label_folder_path,
image_folder_path,
prior_boxes,
prior_boxes_point_form,
batch_size = 8,
n_classes = 5,
image_height = 300,
image_width = 300,
normalize = True,
shuffle = True,
image_extension = '.png',
training = True):
self.list_IDs = list_IDs
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.n_classes = n_classes
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.label_folder_path = label_folder_path
self.image_folder_path = image_folder_path
self.prior_boxes = prior_boxes
self.prior_boxes_point_form = prior_boxes_point_form
self.image_height = image_height
self.image_width = image_width
self.normalize = normalize
self.image_extension = image_extension
self.training = training
self.on_epoch_end()
"""
Inputs:
list_IDs: name of files used to look data in label_folder_path and image_folder_path
label_folder_path: path to where labels are stored, need to be in .txt format
image_folder_path: path to where images are stored, need to be in png
prior_boxes: precalculated prior boxes in (c_x, c_y, w, h)
prior_boxes_point_form: precomputed prior boxes in (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max)
batch_size: int
n_classes: number of classes in the dataset, don't include background
"""
def __len__(self):
return int( np.floor( len(self.list_IDs) / self.batch_size ) )
def __getitem__(self, index):
indexes = self.indexes[index * self.batch_size:(index + 1) * self.batch_size]
list_IDs_temp = [self.list_IDs[k] for k in indexes]
X, y = self.__data_generation(list_IDs_temp)
return X, y
def on_epoch_end(self):
self.indexes = np.arange(len(self.list_IDs))
if self.shuffle:
np.random.shuffle(self.indexes)
def __data_generation(self, list_IDs_temp):
X = np.empty([self.batch_size, self.image_height, self.image_width, 3])
y_label = None
y_loc = None
for i, file_name in enumerate(list_IDs_temp):
image, labelled_gt_box_coords = read_data( file_name,
self.image_folder_path,
self.label_folder_path,
self.image_extension
)
if self.training:
if np.random.rand() > 0.5:
image, labelled_gt_box_coords = returnPatches(image, labelled_gt_box_coords)
if np.random.rand() > 0.5:
image, labelled_gt_box_coords = horizontalFlipImageAndLabels(image, labelled_gt_box_coords)
if np.random.rand() > 0.8:
image, labelled_gt_box_coords = verticalFlipImageAndLabels(image, labelled_gt_box_coords)
# take care of images with no labels
# if no label then the whole image is a background
if len(labelled_gt_box_coords) == 0:
labelled_gt_box_coords = [[0, 0, 0 , image.shape[1], image.shape[0]]]
image, labelled_gt_box_coords = resize_images_and_labels(image, labelled_gt_box_coords, self.image_height, self.image_width)
if self.normalize:
X[i,] = image / self.image_width
else:
X[i,] = image / self.image_width
labelled_gt_box_coords_normallized = label_dimensions_normalized(labelled_gt_box_coords, self.image_height, self.image_width)
gt_labels = [l[0] for l in labelled_gt_box_coords_normallized]
gt_boxes_normalized = [l[1:] for l in labelled_gt_box_coords_normallized]
offset, one_hot_encoded_label = match_priors_with_gt(
self.prior_boxes,
self.prior_boxes_point_form,
tf.constant([gt_boxes_normalized]),
tf.constant([gt_labels]),
number_of_labels = self.n_classes + 1,
threshold = 0.5)
if y_label == None:
y_label = one_hot_encoded_label
y_loc = offset
else:
y_label = tf.concat([y_label, one_hot_encoded_label], axis = 0)
y_loc = tf.concat([y_loc, offset], axis = 0)
return X, [y_loc, y_label]
Implementing SSD Loss
Once we have matched the ground truth boxes with the default boxes. Most of the default boxes will end up being negatives. As a result, the labels will end up being significantly imbalanced. To deal with this imbalance, we use a technique called negative mining. Instead of using all of the negative training examples we sort the softmax confidence metric for each default box and pick the top ones so that the ratio between negatives and positive is at most 3:1.
class SSDLoss:
def __init__(self, negative_mining_ratio = 3, alpha = 1.0):
self.negative_mining_ratio = negative_mining_ratio
self.alpha = alpha
# From https://github.com/pierluigiferrari/ssd_keras/blob/master/keras_loss_function/keras_ssd_loss.py
def smooth_L1_loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
'''
Compute smooth L1 loss, see references.
Arguments:
y_true (nD tensor): A TensorFlow tensor of any shape containing the ground truth data.
In this context, the expected tensor has shape `(batch_size, #boxes, 4)` and
contains the ground truth bounding box coordinates, where the last dimension
contains `(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)`.
y_pred (nD tensor): A TensorFlow tensor of identical structure to `y_true` containing
the predicted data, in this context the predicted bounding box coordinates.
Returns:
The smooth L1 loss, a nD-1 Tensorflow tensor. In this context a 2D tensor
of shape (batch, n_boxes_total).
References:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.08083
'''
absolute_loss = tf.abs(y_true - y_pred)
square_loss = 0.5 * (y_true - y_pred)**2
l1_loss = tf.where(tf.less(absolute_loss, 1.0), square_loss, absolute_loss - 0.5)
return tf.reduce_sum(l1_loss, axis=-1)
# From https://github.com/pierluigiferrari/ssd_keras/blob/master/keras_loss_function/keras_ssd_loss.py
def log_loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
'''
Compute the softmax log loss.
Arguments:
y_true (nD tensor): A TensorFlow tensor of any shape containing the ground truth data.
In this context, the expected tensor has shape (batch_size, #boxes, #classes)
and contains the ground truth bounding box categories.
y_pred (nD tensor): A TensorFlow tensor of identical structure to `y_true` containing
the predicted data, in this context the predicted bounding box categories.
Returns:
The softmax log loss, a nD-1 Tensorflow tensor. In this context a 2D tensor
of shape (batch, n_boxes_total).
'''
# Make sure that `y_pred` doesn't contain any zeros (which would break the log function)
y_pred = tf.maximum(y_pred, 1e-15)
# Compute the log loss
log_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(y_true * tf.math.log(y_pred), axis=-1)
return log_loss
def localization_loss(self, actual_deltas, pred_delta):
"""
input:
actual_deltas: (batch_size, number of prior boxes, [delta_cx, delta_cy, delta_w, delta_h, pos_cond])
pred_delta = (batch_size, number of prior boxes, [delta_cx, delta_cy, delta_w, delta_h])
outputs:
loc_loss: Huber loss over all prior boxes with IOU > threshold (defined elsewhere)
over ground label boxes
"""
batch_size = tf.shape(pred_delta)[0]
localization_loss_for_all_priors = self.smooth_L1_loss(actual_deltas[:, :, :4], pred_delta)
localization_loss_for_all_priors = tf.cast(localization_loss_for_all_priors, tf.float32)
# localization loss is only for default prior boxes with IOU > 0.5 over ground truth boxes
localization_loss_for_all_priors = localization_loss_for_all_priors * actual_deltas[:, :, 4]
total_pos_boxes = tf.reduce_sum(actual_deltas[:, :, 4:], axis=1)
# If an image has no labels, the loc loss for that image should be 0.
no_label_mask = tf.reduce_any( tf.not_equal(total_pos_boxes, tf.constant(0.)), axis = 1 )
total_pos_boxes = tf.where(total_pos_boxes <= 0, 1e-6, total_pos_boxes)
loss = self.alpha * tf.where(tf.transpose([no_label_mask]),
localization_loss_for_all_priors / total_pos_boxes,
tf.constant(0.))
return tf.reduce_sum(loss, axis = 1) * tf.cast(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
def confidence_loss(self, actual_labels, pred_labels):
"""
inputs:
actual_labels = (batch_size, number of prior boxes, total labels)
pred_labels = (batch_size, number of prior boxes, total labels)
outputs:
conf_loss = loss per class
"""
batch_size = tf.shape(pred_labels)[0]
confidence_loss_for_all = self.log_loss(actual_labels, pred_labels)
confidence_loss_for_all = tf.cast(confidence_loss_for_all, tf.float32)
pos_cond = tf.reduce_any( tf.equal(actual_labels[..., 1:], tf.constant(1.0)), axis = 2)
pos_mask = tf.cast(pos_cond, dtype=tf.float32)
total_pos_boxes = tf.reduce_sum(pos_mask, axis=1)
pos_loss = pos_mask * confidence_loss_for_all
# hard negative mining
# set positive cases to 0
neg_cond = tf.reduce_any( tf.equal(actual_labels[..., :1], tf.constant(1.0)), axis = 2)
confidence_loss_for_all = tf.where(neg_cond, confidence_loss_for_all,
tf.constant(0., tf.float32)
)
# If there are no positive positive boxes in the select top k
neg_boxes_for_empty_images = 0
total_neg_boxes = tf.cast(total_pos_boxes * self.negative_mining_ratio, tf.int32)
no_neg_boxes_mask = tf.not_equal(total_neg_boxes, tf.constant(0))
total_neg_boxes = tf.where(no_neg_boxes_mask, total_neg_boxes, tf.constant(neg_boxes_for_empty_images))
# sort by positive example
loss_sorted_indices = tf.argsort(confidence_loss_for_all, direction="DESCENDING")
loss_sorted_rank = tf.argsort(loss_sorted_indices)
neg_mining_cond = tf.less(loss_sorted_rank, tf.expand_dims(total_neg_boxes, axis=1))
neg_mining_mask = tf.cast(neg_mining_cond, dtype=tf.float32)
neg_loss = neg_mining_mask * confidence_loss_for_all
# total_boxes = total_pos_boxes + tf.cast(total_neg_boxes, tf.float32)
total_pos_boxes = tf.where(total_pos_boxes <= 0, 1e-6, total_pos_boxes)
total_loss = (pos_loss + neg_loss) / tf.expand_dims(total_pos_boxes, axis = 1)
return tf.reduce_sum(total_loss, axis = 1) * tf.cast(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
Model Training Results
I trained the model for a couple of thousand epochs on the VOC2012 datasets. The performance of the model is a bit hit and miss on real out-of-sample dataset as you can see from the images below:
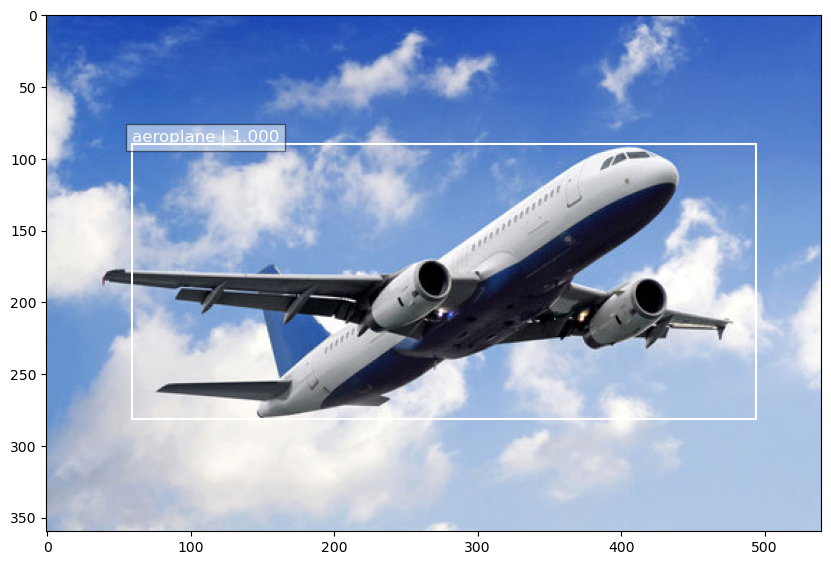
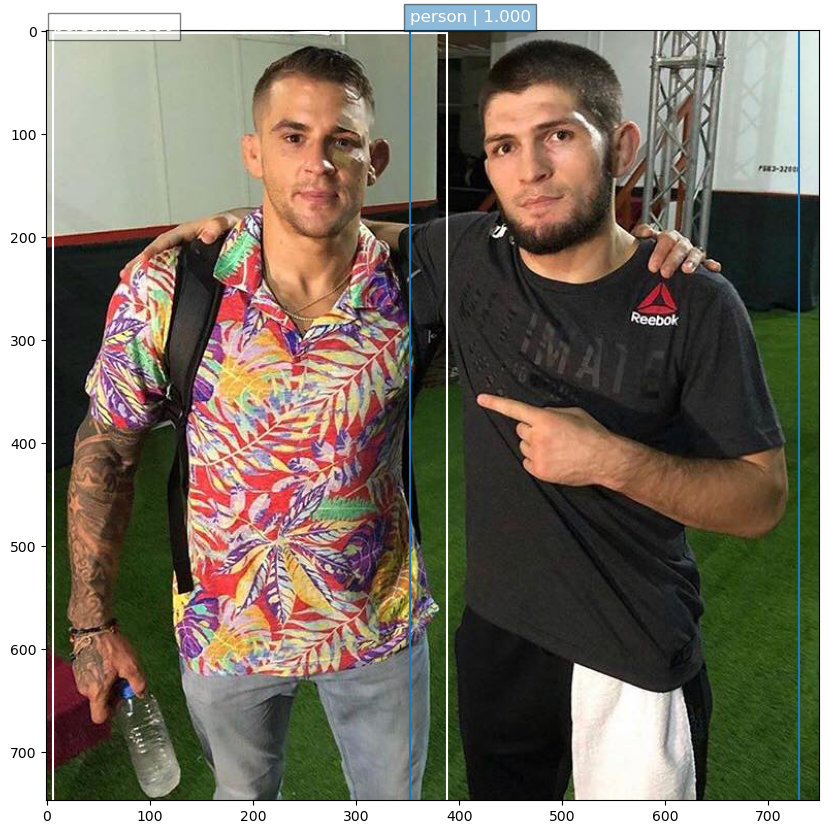
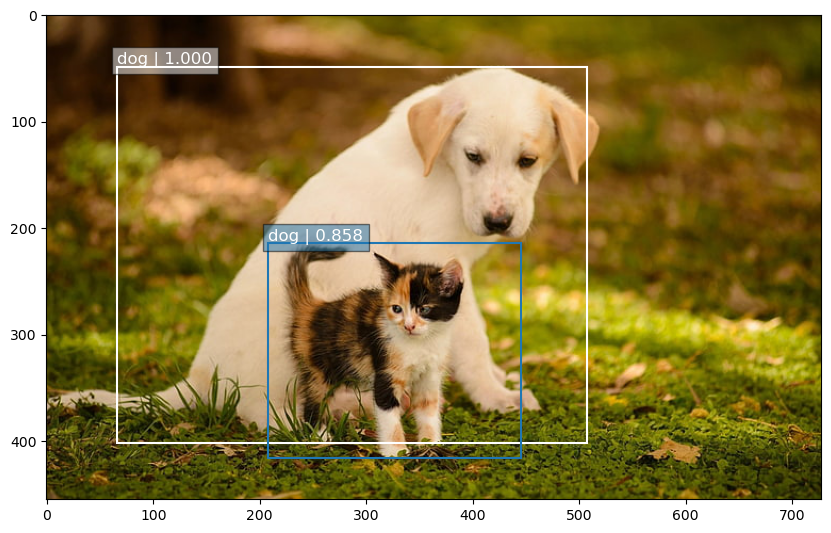



My goal is to use this as a starting point for a larger project I am working on so I didn’t train the model further. I just wanted to make sure that the model is implemented correctly, I am sure if I train for a longer periof of time I will see an improvement in performance.
To learn more check out my github repo here for the complete implementation.
Comments